The
Surface of the Earth
The Earth’s crust is broken up into smaller
pieces called tectonic plates.
These plates can move around by a few centimetres a year.
The crust and the very top of the mantle (just
below and touching the underside of the crust) make up an area called the lithosphere.
Convection
currents within the lithosphere cause the crust to move.
Heat
released by radioactive decay in the mantle causes convection
currents. The hot rock rises then
cools and sinks again.
The hot
rock will rise and cause friction on the underside of the crust, moving it by a
few cm a year.
From the
diagram of the lithosphere the plates are moving apart at point 1 and together
at point 2.
Billions
of year ago the Earth was thought to be made up of one land mass called
‘Pangea’. Over time the plates moved due
to convection currents to form the continents as we know them now.
What
happens at plate boundaries?
1.)
Plates colliding
When the
plates collide the more dense plate sinks forcing the less dense
plate upwards, making a fold mountain, sometime volcanoes form if
the more dense plate melts and the magma rises.
If the volcano erupts is causes damage to the surface of the Earth and
the habitats that are found there.
This is
known as a destructive plate boundary.
An
example of where this is occurring is on the west coast of South America, where
the Nazca plate is colliding with the South American plate forming the Andes Mountains.
2.)
Plates moving apart
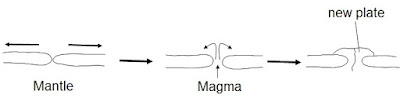
When the
plates move apart magma rises and fills the gap. This cools forming new plate. This process will happen continually.
This is
known as a constructive plate boundary.
An
example of where this is occurring is under the Atlantic Ocean, where the new
plate that forms makes up the Mid Atlantic ridge. So America and the UK are moving further
apart from each other.
3.)
Plates sliding past each other
This
happens when plates are moving side by side, sometimes they get caught together
until the pressure is too great and they move suddenly. This causes an earthquake.
This is
known as a conservative plate boundary.
An
example of where this is occurring is along the Californian coast. The San Andreas Fault in San Francisco.
If
movements occur suddenly at plate boundaries earthquakes and/or volcanic
eruptions can occur. This can cause severe devastation to the surface of the
Earth and to habitats in the area.
The
surface of the earth has been changed naturally over time by processes such as:
- Asteroid impact - This would create large craters in the surface of the Earth, along with destroying objects and habitats and has been attributed to be the cause for certain mass extinctions in the planet's history, including the dinosaurs. The effects of asteroid collisions have been shown in the films 'Armageddon' and 'Deep Impact'.
- Volcanic eruption - In 1980 Mount St Helens erupted changing the landscape of the mountain and surrounding areas. Soils become more fertile as the lava and ash contain vital nutrient elements such as sulfur and phosphorus.
- Earthquakes - These have the ability to change the landscape. In 1958 at Lituya Bay, Alaska, an earthquake caused a landslide that shifted so much material into the bay that it caused a mega-tsunami (500m high wave). This wave destroyed the whole shoreline of the bay. Another example of an earthquake that caused a tsunami in 2011 was one that happened off the north-east coast of Japan (http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-12709598). This caused devastation and loss of life, also causing critical damage to a nuclear power plant.
- Erosion - this can happen by air, water (ice) or biological action.
- During a number of ice ages, large ice masses called glaciers moved from high in mountain regions to lower regions over millions of years, carving deep channels into the surface and breaking up and depositing rocky masses along the way.
Read more by
clicking the following link:





No comments:
Post a Comment